 | ||
Mitigation Measures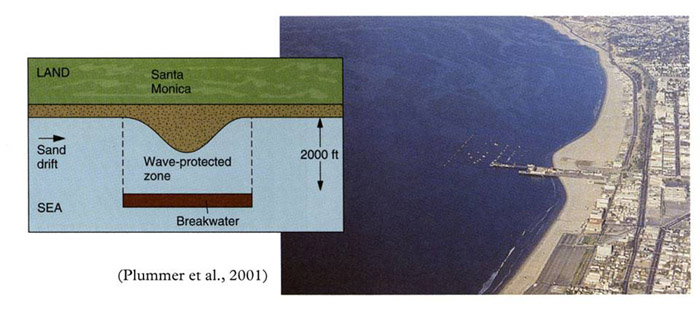 Figure 33 : Breakwalls Breakwalls are built parallel to the shoreline and absorb some energy from the waves. They are usually built in front of shoreline to allow it still to be navigatable such as marinas. 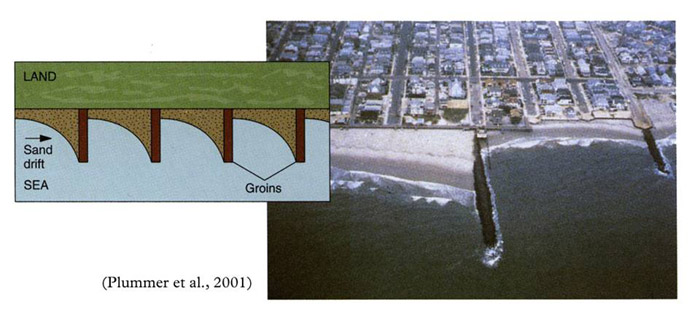 Figure 34 : Groins / Groynes Groynes are built perpendicular to the shoreline to slow down longshore transport of sediment. It is an effective technique and is often used to provide sediment to beaches. 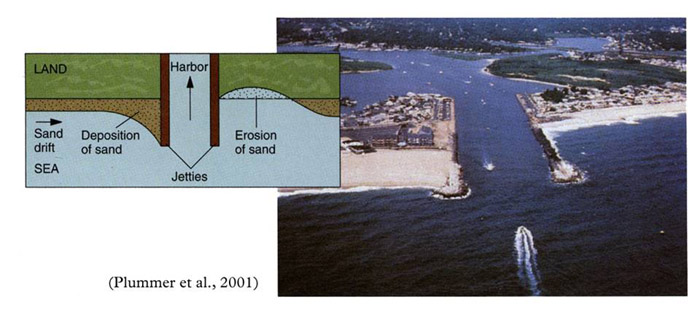 Figure 35 : Jetties Jetties are usually placed at the entry point of a harbor. Their main purpose is to reduce the amount of dredging required at the entrance of a harbor. Dredging is still required, but is required less often. They usually result in deposition of sediment on the upcurrent side, and starve the downcurrent side of sediment.
|
