
Different electromagnetic portions of the spectrum provide insight into each of the meteorological variables. Included in the meteorological variables that remote sensing can observe are ocean currents, roughness and sea surface temperatures, forest fires, precipitation, distribution of snow and ice, atmospheric temperature, humidity, temperture of underlying surface, tropical cyclone coordinates, wind speed and direction, and atmospheric gasses and pollutants.
Cloud Cover
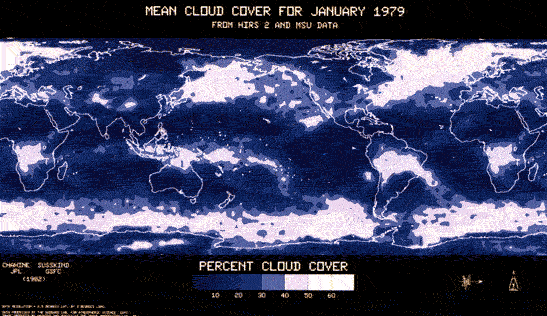
Cloud Top Pressure
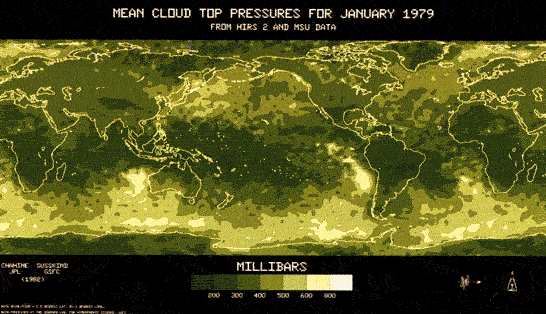
Cloud Temperature
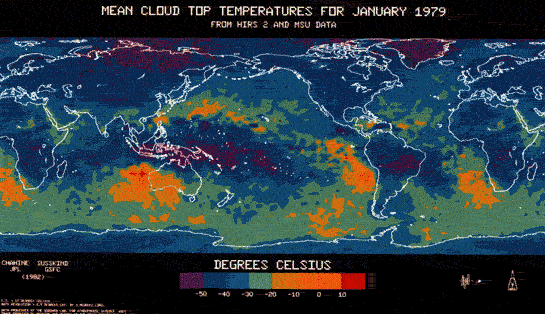
Global cloud climatology products derived from infra-red and microwave sounders on NOAA polar-orbiting satellites (Barrett, et al., 1999, Plate 5)
Radiation Flux
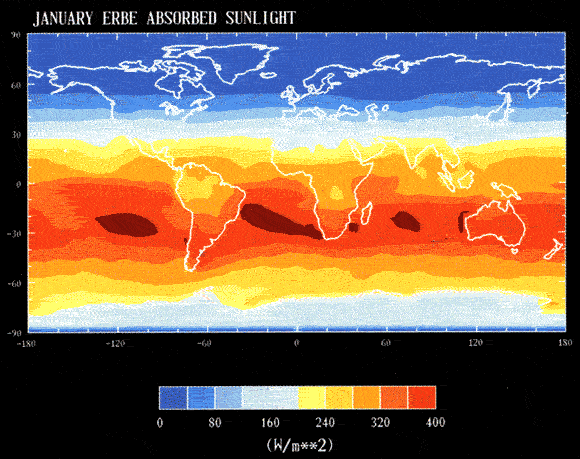
False color contour map of the five-year mean values of solar radiation flux absorbed by the Earth in January (Wm^2), derived from satellite measurements made by the Earth Radiation Budget Experiment (ERBE) (Hoffman, et al., 2001)